

They include medicines such as aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, diclofenac, and celecoxib. NSAIDs are commonly used to relieve pain and reduce fevers. This can lead to low levels of amniotic fluid surrounding the baby and possible complications. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is warning that use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) around 20 weeks or later in pregnancy may cause rare but serious kidney problems in an unborn baby. A normal single deepest pocket is 2 cm to 8 cm (less than 2 cm is oligohydramnios, greater than 8 cm is polyhydramnios).The U.S. The entire uterus should be examined, and the single deepest vertical pocket of fluid should be identified and measured. The technique used to measure a single deepest pocket (also referred to as a maximum vertical pocket) is identical to the measurement of amniotic fluid amounts in the four quadrants used to determine an amniotic fluid index.

In pregnancies less than 24 weeks, or with multiple gestations, a single deepest pocket is used. The calipers may not cross over any segments of the umbilical cord or any fetal parts.Īlternative Measurements of Amniotic Fluid Volume Color Doppler is typically placed over the pocket of fluid to ensure that the pocket does not contain any segments of the umbilical cord, which are not always well seen in B-mode (standard 2D greyscale) imaging. The deepest vertical pocket of fluid in each quadrant should be identified and measured, and these four measurements should be added together to calculate the total amniotic fluid index. This ensures that each pocket of fluid is being measured in the same plane.
Causes of low amniotic fluid skin#
The ultrasound transducer should be held perpendicular to the patient's spine, not perpendicular to the patient's skin as is performed in most other ultrasounds, and should be maintained in an axial plane (notch to the patient's right). Each quadrant should be examined systematically. The uterus should be divided into four quadrants to assess amniotic fluid index. Many cases of polyhydramnios are idiopathic, meaning no definite cause is identified. In these cases, it may be associated with fetal macrosomia. Increased amniotic fluid production occurs as a result of fetal polyuria, such as in uncontrolled maternal diabetes with persistently elevated maternal blood sugars. This can occur due to gastrointestinal malformations, fetal neurologic problems such as anencephaly, or mechanical obstruction of the esophagus by other intrathoracic processes. If the fetus is unable to swallow the typical amounts of amniotic fluid, this can lead to polyhydramnios. The normal fetus is constantly swallowing amniotic fluid and urinating to create more fluid. Oligohydramnios can also occur because the patient's amniotic membrane has ruptured and amniotic fluid is leaking out of the uterus. Therefore, decreased amniotic fluid volume due to decreased urine production by the fetal kidney is a reflection of chronic hypoperfusion of the fetus. When the fetus receives inadequate nutrients and oxygen from the placenta, blood is shunted away from the fetal kidney, glomerular filtration rate decreases, and urinary output decreases.

It is the same mechanism that causes oliguria in critically ill adults. Decreased urine production by the fetal kidney typically reflects inadequate blood flow to the fetal kidney, caused by shunting of fetal blood flow away from the kidney to the heart and brain.
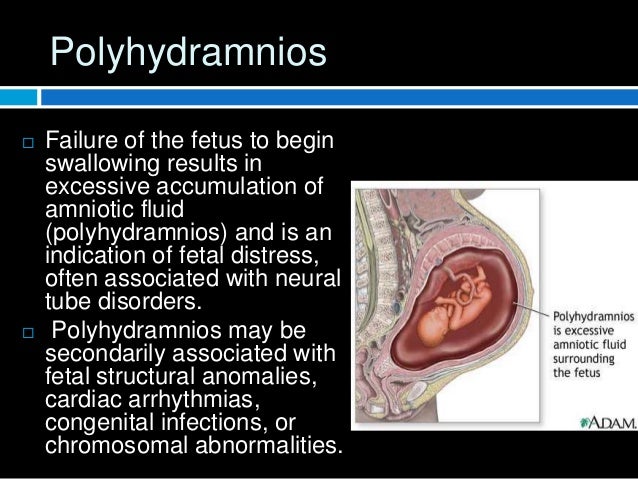
Urinary tract obstruction can occur anywhere along the fetal urinary tract and can be catastrophic for the fetus. Decreased fetal urine output can have a number of causes, which fall into two general categories: fetal urinary tract obstruction and decreased urine production by the fetal kidney.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
